Linbox Rescue Server is a centralized PC hardware/software inventory, imaging, and backup tool. The Linbox Rescue Server (LRS) is a tool to centralize hard disk images, file backups, hardware inventory, Windows PCs software inventory, and remote access on a single server.It can be managed from any PC through a Web-based administration interface, and disk images can be restored using PXE boot.
AOMEI PXEBoot Free is a best tool to start up multiple client computers within LAN through the network by using bootable image on a server-side computer for system maintenance. It supports Windows 10, Windows 8/8.1, Windows 7, XP, and Vista.
- File Name:PXEBoot.exe
- Author:AOMEI Technology Co., Ltd
- License:Freeware (Free)
- File Size:12.52 Mb
- Runs on:WinXP, WinVista, WinVista x64, Win7 x32, Win7 x64, Other, Windows Vista
emBoot's boot agents for VMware are client-based 'virtual' firmware that allows a VMware client VM to do a 'network boot? using the virtual NIC. Our boot agents for VMware are fully compliant with the Intel Wired for Management - Preboot Execution. ...
- File Name:PXE Boot Image for VMware,floppy image
- Author:emBoot Incorporated
- License:Shareware ($9.00)
- File Size:67 Kb
- Runs on:Win NT 4.x, XP, 2000, 2003, Linux
TSUthin is a document and software for Windows Terminal Services Client diskless computer network clients. It is used to boot (diskless) workstations over a network using PXEboot. ISO file for download only available to burn on the CD.
- File Name:tsuthin.exe
- Author:Admin Pains
- License:Data only ($50.00)
- File Size:10.85 Mb
- Runs on:Not Applicable
CCBoot, from www.ccboot.com, is thin client software with pxeboot tech and Internet cafe software with diskless system, also works for schools and offices, which helps restore a clean system after each reboot and update all PC's with a single click.
- File Name:ccbootsetup.exe
- Author:CCBoot
- License:Shareware ($25.00)
- File Size:9.1 Mb
- Runs on:WinXP, Win7 x32, Win7 x64, Windows 8, Windows2003, Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008r2, Windows Server 2012
A small utility to quickly and easily make the changes required to your Configuration Manager Distribution Points settings to enable a faster PXE boot up time..
- File Name:DPPXEBoot.zip
- Author:TechyGeeksHome
- License:Freeware (Free)
- File Size:67 Kb
- Runs on:Win2000, WinXP, Win7 x32, Win7 x64, Windows 8, WinServer, WinOther, WinVista, WinVista x64
Network Boot Tools offers a pre-OS and network boot management solution that helps business enterprises lower their total cost of ownership of their networks. This product allows network administrators to remotely manage client PCs on their network. ...
- File Name:NetworkBootTools_Trial.sh
- Author:emBoot Incorporated
- License:Shareware ($149.99)
- File Size:1.96 Mb
- Runs on:Win 95, 98, NT 4.x, XP, 2000
A web based GUI for managing PXE boot. Also supports creating and serving Kickstart scripts. This provides a client install in one click.
- File Name:ock-0.55.tar.gz
- Author:sigbjornl
- License:Shareware ($)
- File Size:9.92 Mb
- Runs on:WinXP, Win2000, Win Vista, Windows 7
Cloneboot is a series of text files and shell scripts that can of clone a Linux installation onto identical hardware by formatting and copying the hard disk during a PXEboot process.
- File Name:cloneboot
- Author:Michael James
- License:Freeware (Free)
- File Size:
- Runs on:Windows
WinAgents TFTP Server for Windows is a full-service TFTP server realized as a Windows service. Using WinAgents TFTP Server, you can make reserve copies of device settings, update flash images, store sound files for IVR systems and do many other thing. ...
- File Name:tftpsetup.exe
- Author:WinAgents Software Group
- License:Shareware ($99.00)
- File Size:4.65 Mb
- Runs on:WinXP, Windows2000, Windows2003, Windows Vista
Linbox Rescue Server is a centralized PC hardware/software inventory, imaging, and backup tool. The Linbox Rescue Server (LRS) is a tool to centralize hard disk images, file backups, hardware inventory, Windows PCs software inventory, and remote access on a single server.It can be managed from any PC through a Web-based administration interface, and disk images can be restored using PXE boot and Multicast TFTP, or using a bootable CD or DVD.
- File Name:base-update_20070703.tgz
- Author:Linbox
- License:Freeware (Free)
- File Size:4.28 Mb
- Runs on:Linux
The Windows XP startup disk allows computers without a bootable CD-ROM to perform a new installation of the operating system. The Windows XP startup disk will automatically load the correct drivers to gain access to the CD-ROM drive and start a new installation of Setup.The Windows XP startup disk allows computers without a bootable CD-ROM to perform a new installation of the operating system.
- File Name:WinXP_EN_HOM_BF.EXE
- Author:Microsoft Corporation.
- License:Freeware (Free)
- File Size:4.18 Mb
- Runs on:WinNT 4.x, WinNT 3.x, WinME, Win2003, Win2000, Win98, Win95
emBoot's MBA for Realtek is client-based firmware that allows a client PC to do a 'network boot? using the NIC or LAN-On-Motherboard. MBA for Realtek is fully compliant with the Intel Wired for Management PXE spec.* Simple means of desktop OS. ...
- File Name:MBAoD_Realtek_Trial.sh
- Author:emBoot Incorporated
- License:Shareware ($7.00)
- File Size:69 Kb
- Runs on:Win NT 4.x, XP, 2000, 2003, Linux, MS-DOS
Related:Server Pxe Boot - Pxe Boot Disc - Pxe Boot Pos - Pxe Boot Roms - Pxe Boot Tool
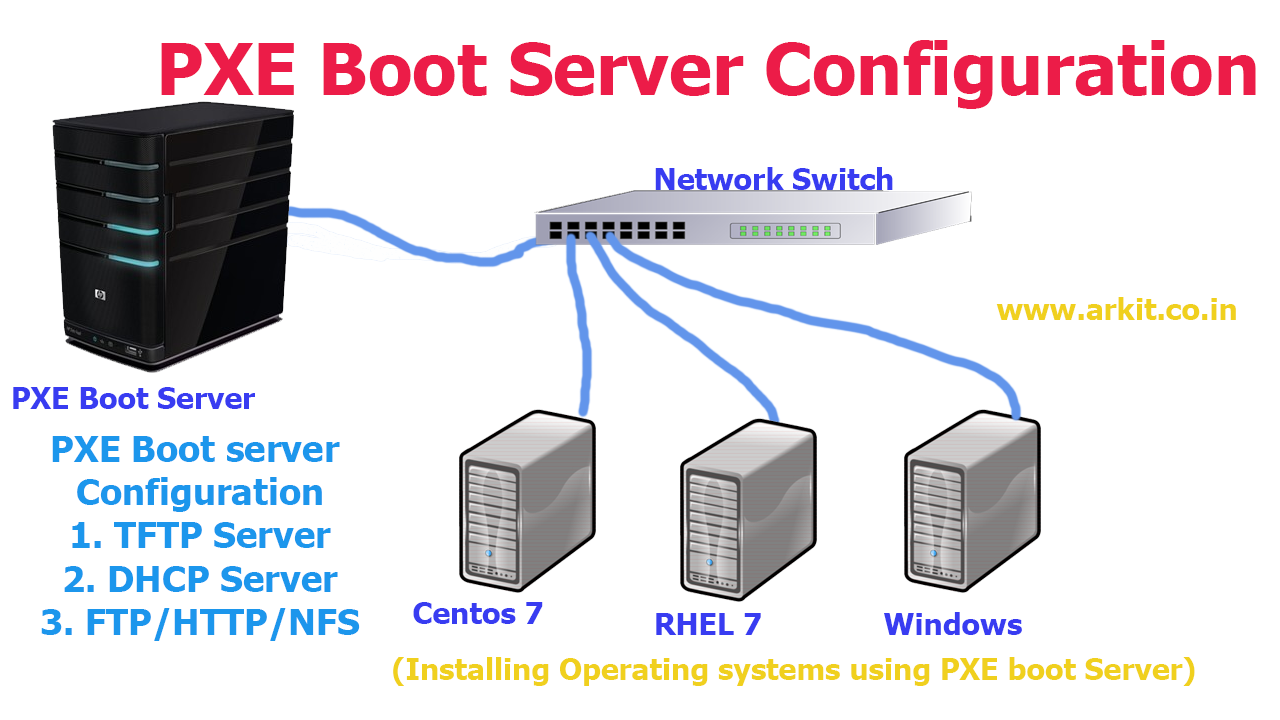
PXE Server – Preboot eXecution Environment – instructs a client computer to boot, run or install an operating system directly form a network interface, eliminating the need to burn a CD/DVD or use a physical medium, or, can ease the job of installing Linux distributions on your network infrastructure on multiple machines the same time.
Requirements
This article will explain how you can install and configure a PXE Server on RHEL/CentOS 7 x64-bit with mirrored local installation repositories, sources provided by CentOS 7 DVD ISO image, with the help of DNSMASQ Server.
Which provides DNS and DHCP services, Syslinux package which provides bootloaders for network booting, TFTP-Server, which makes bootable images available to be downloaded via network using Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) and VSFTPD Server which will host the local mounted mirrored DVD image – which will act as an official RHEL/CentOS 7 mirror installation repository from where the installer will extract its required packages.
Step 1: Install and configure DNSMASQ Server
1. No need to remind you that is absolutely demanding that one of your network card interface, in case your server poses more NICs, must be configured with a static IP address from the same IP range that belongs to the network segment that will provide PXE services.
So, after you have configured your static IP Address, updated your system and performed other initial settings, use the following command to install DNSMASQ daemon.
Install dnsmasq Package
2. DNSMASQ main default configuration file located in /etc directory is self-explanatory but intends to be quite difficult to edit, do to its highly commented explanations.
First make sure you backup this file in case you need to review it later and, then, create a new blank configuration file using your favorite text editor by issuing the following commands.
3. Now, copy and paste the following configurations on dnsmasq.conf file and assure that you change the below explained statements to match your network settings accordingly.
The statements that you need to change are follows:
- interface – Interfaces that the server should listen and provide services.
- bind-interfaces – Uncomment to bind only on this interface.
- domain – Replace it with your domain name.
- dhcp-range – Replace it with IP range defined by your network mask on this segment.
- dhcp-boot – Replace the IP statement with your interface IP Address.
- dhcp-option=3,192.168.1.1 – Replace the IP Address with your network segment Gateway.
- dhcp-option=6,92.168.1.1 – Replace the IP Address with your DNS Server IP – several DNS IPs can be defined.
- server=8.8.4.4 – Put your DNS forwarders IPs Addresses.
- dhcp-option=28,10.0.0.255 – Replace the IP Address with network broadcast address –optionally.
- dhcp-option=42,0.0.0.0 – Put your network time servers – optionally (0.0.0.0 Address is for self-reference).
- pxe-prompt – Leave it as default – means to hit F8 key for entering menu 60 with seconds wait time..
- pxe=service – Use x86PC for 32-bit/64-bit architectures and enter a menu description prompt under string quotes. Other values types can be: PC98, IA64_EFI, Alpha, Arc_x86, Intel_Lean_Client, IA32_EFI, BC_EFI, Xscale_EFI and X86-64_EFI.
- enable-tftp – Enables the build-in TFTP server.
- tftp-root – Use /var/lib/tftpboot – the location for all netbooting files.
For other advanced options concerning configuration file feel free to read dnsmasq manual.
Step 2: Install SYSLINUX Bootloaders
4. After you have edited and saved DNSMASQ main configuration file, go ahead and install Syslinx PXE bootloader package by issuing the following command.
Install Syslinux Bootloaders
5. The PXE bootloaders files reside in /usr/share/syslinux absolute system path, so you can check it by listing this path content. This step is optional, but you might need to be aware of this path because on the next step, we will copy of all its content to TFTP Server path.
Step 3: Install TFTP-Server and Populate it with SYSLINUX Bootloaders
6. Now, let's move to next step and install TFTP-Server and, then, copy all bootloders files provided by Syslinux package from the above listed location to /var/lib/tftpboot path by issuing the following commands.
Install TFTP Server
Step 4: Setup PXE Server Configuration File
7. Typically the PXE Server reads its configuration from a group of specific files (GUID files – first, MAC files – next, Default file – last) hosted in a folder called pxelinux.cfg, which must be located in the directory specified in tftp-root statement from DNSMASQ main configuration file.
Create the required directory pxelinux.cfg and populate it with a default file by issuing the following commands.
8. Now it's time to edit PXE Server configuration file with valid Linux distributions installation options. Also note that all paths used in this file must be relative to the /var/lib/tftpboot directory.

For other advanced options concerning configuration file feel free to read dnsmasq manual.
Step 2: Install SYSLINUX Bootloaders
4. After you have edited and saved DNSMASQ main configuration file, go ahead and install Syslinx PXE bootloader package by issuing the following command.
Install Syslinux Bootloaders
5. The PXE bootloaders files reside in /usr/share/syslinux absolute system path, so you can check it by listing this path content. This step is optional, but you might need to be aware of this path because on the next step, we will copy of all its content to TFTP Server path.
Step 3: Install TFTP-Server and Populate it with SYSLINUX Bootloaders
6. Now, let's move to next step and install TFTP-Server and, then, copy all bootloders files provided by Syslinux package from the above listed location to /var/lib/tftpboot path by issuing the following commands.
Install TFTP Server
Step 4: Setup PXE Server Configuration File
7. Typically the PXE Server reads its configuration from a group of specific files (GUID files – first, MAC files – next, Default file – last) hosted in a folder called pxelinux.cfg, which must be located in the directory specified in tftp-root statement from DNSMASQ main configuration file.
Create the required directory pxelinux.cfg and populate it with a default file by issuing the following commands.
8. Now it's time to edit PXE Server configuration file with valid Linux distributions installation options. Also note that all paths used in this file must be relative to the /var/lib/tftpboot directory.
Below you can see an example configuration file that you can use it, but modify the installation images (kernel and initrd files), protocols (FTP, HTTP, HTTPS, NFS) and IPs to reflect your network installation source repositories and paths accordingly.
Add the following whole excerpt to the file.
As you can see CentOS 7 boot images (kernel and initrd) reside in a directory named centos7 relative to /var/lib/tftpboot (on an absolute system path this would mean /var/lib/tftpboot/centos7) and the installer repositories can be reached by using FTP protocol on 192.168.1.20/pub network location – in this case the repos are hosted locally because the IP address is the same as the PXE server address).
Also menu label 3 specifies that the client installation should be done from a remote location via VNC (here replace VNC password with a strong password) in case you install on a headless client and the menu label 2 specifies as
installation sources a CentOS 7 official Internet mirror (this case requires an Internet connection available on client through DHCP and NAT).
Important: As you see in the above configuration, we've used CentOS 7 for demonstration purpose, but you can also define RHEL 7 images, and following whole instructions and configurations are based on CentOS 7 only, so be careful while choosing distribution.
Step 5: Add CentOS 7 Boot Images to PXE Server
9. For this step CentOS kernel and initrd files are required. To get those files you need the CentOS 7 DVD ISO Image. So, go ahead and download CentOS DVD Image, put it in your DVD drive and mount the image to /mnt system path by issuing the below command.
The reason for using the DVD and not a Minimal CD Image is the fact that later this DVD content would be used to create the
locally installer repositories for FTP sources.
Mount CentOS DVD
If your machine has no DVD drive you can also download CentOS 7 DVD ISO locally using wget or curl utilities from a CentOS mirror and mount it.
10. After the DVD content is made available, create the centos7 directory and copy CentOS 7 bootable kernel and initrd images from the DVD mounted location to centos7 folder structure.
The reason for using this approach is that, later you can create new separate directories in /var/lib/tftpboot path and add other Linux distributions to PXE menu without messing up the entire directory structure.
Step 6: Create CentOS 7 Local Mirror Installation Source
11. Although you can setup Installation Source Mirrors via a variety of protocols such as HTTP, HTTPS or NFS, for this guide, I have chosen FTP protocol because is very reliable and easy to setup with the help of vsftpd server.
Further install vsftpd daemon, copy all DVD mounted content to vsftpd default server path (/var/ftp/pub) – this can take a while depending on your system resources and append readable permissions to this path by issuing the following commands.
Install Vsftpd Server
Set Permissions on FTP Path
Step 7: Start and Enable Daemons System-Wide
Pxe Boot Windows
12. Now that the PXE server configuration is finally finished, start DNSMASQ and VSFTPD servers, verify their status and enable it system-wide, to automatically start after every system reboot, by running the below commands.
Start Vsftpd Service
Step 8: Open Firewall and Test FTP Installation Source
13. To get a list of all ports that needs to be open on your Firewall in order for client machines to reach and boot from PXE server, run netstat command and add CentOS 7 Firewalld rules accordingly to dnsmasq and vsftpd listening ports.
Open Ports in Firewall
14. To test FTP Installation Source network path open a browser locally (lynx should do it) or on a different computer and type the IP Address of your PXE server with
FTP protocol followed by /pub network location on URL filed and the result should be as presented in the below screenshot.
15. To debug PXE server for eventual misconfigurations or other information and diagnostics in live mode run the following command.
Check PXE Logs for Errors
16. Finally, the last required step that you need to do is to unmount CentOS 7 DVD and remove the physical medium.
Step 9: Configure Clients to Boot from Network
17. Now your clients can boot and install CentOS 7 on their machines by configuring Network Boot as primary boot device from their systems BIOS or by hitting a specified key during BIOS POST operations as specified in motherboard manual.
In order to choose network booting. After first PXE prompt appears, press F8 key to enter presentation and then hit Enter key to proceed forward to PXE menu.
PXE Network OS Boot
18. Once you have reached PXE menu, choose your CentOS 7 installation type, hit Enter key and continue with the installation procedure the same way as you might install it from a local media boot device.
Please note down that using variant 2 from this menu requires an active Internet connection on the target client. Also, on below
screenshots you can see an example of a client remote installation via VNC.
Pxe Boot Server Windows
Remote Linux Installation via VNC
That's all for setting up a minimal PXE Server on CentOS 7. On my next article from this series, I will discuss other issues concerning this PXE server configuration such as how to setup automated installations of CentOS 7 using Kickstart files and adding other Linux distributions to PXE menu – Ubuntu Server and Debian 7.
